Understanding Thermogenesis: How Your Body Generates Heat
Thermogenesis is the process by which your body generates heat․ It’s a fundamental aspect of metabolism, crucial for maintaining a stable core temperature regardless of the external environment․ Several factors influence thermogenesis, including muscle activity, digestion, and hormonal activity․ Even small movements contribute to heat production, as does the breakdown of food for energy․
A key player in thermogenesis is brown adipose tissue, or brown fat․ Unlike white fat, which stores energy, brown fat burns calories to generate heat․ This process is particularly activated in cold environments․ Understanding the interplay of these factors—muscle activity, digestion, hormonal influence, and the role of brown fat—offers insights into how our bodies maintain thermal equilibrium․
This intricate process is essential for survival, ensuring optimal function even in fluctuating temperatures․ By understanding the mechanisms of thermogenesis, we can better appreciate the body’s remarkable ability to adapt and thrive․
The Power of Cold: Activating Brown Fat and Boosting Metabolism
Cold exposure has emerged as a powerful tool for activating brown fat and boosting metabolism․ While shivering is a short-term response to cold, generating heat through muscle contractions, brown fat activation offers a more sustainable thermogenic pathway․ When subjected to cold temperatures, brown fat kicks into high gear, burning calories to produce warmth and maintain core body temperature․ This process not only helps us adapt to colder environments but also offers intriguing metabolic benefits․
Research suggests that regular cold exposure can increase the amount and activity of brown fat in the body․ This increase in brown fat activity translates to a higher metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even at rest․ This effect is particularly promising for weight management and improving metabolic health․ Furthermore, cold exposure can improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and preventing metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes․ The enhanced insulin sensitivity allows cells to utilize glucose more efficiently, reducing the risk of insulin resistance․
Beyond the metabolic benefits, cold exposure can also enhance cardiovascular health․ Studies have shown that regular cold plunges or cold showers can improve circulation and lower blood pressure․ The initial vasoconstriction caused by cold is followed by vasodilation, which improves blood flow and strengthens blood vessels․ This vascular response can contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system over time․
The mechanisms behind cold-induced thermogenesis involve complex hormonal and neurological pathways․ Cold exposure activates the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the release of norepinephrine․ Norepinephrine then acts on brown fat cells, stimulating their thermogenic activity․ This intricate cascade of events highlights the body’s remarkable ability to adapt to environmental challenges and harness cold exposure for metabolic benefit․
Incorporating cold exposure into your routine can be as simple as taking cold showers, ending your showers with a blast of cold water, or even immersing yourself in cold water baths․ Start gradually and listen to your body, gradually increasing the duration and intensity of cold exposure․ While the initial shock might be uncomfortable, the long-term benefits for metabolism, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being make exploring the power of cold a worthwhile endeavor․
While promising, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and optimal protocols for cold exposure therapy․ However, the current evidence strongly suggests that harnessing the power of cold can be a valuable tool for optimizing metabolic health and enhancing overall well-being․ Embrace the chill and unlock the potential of cold-induced thermogenesis․
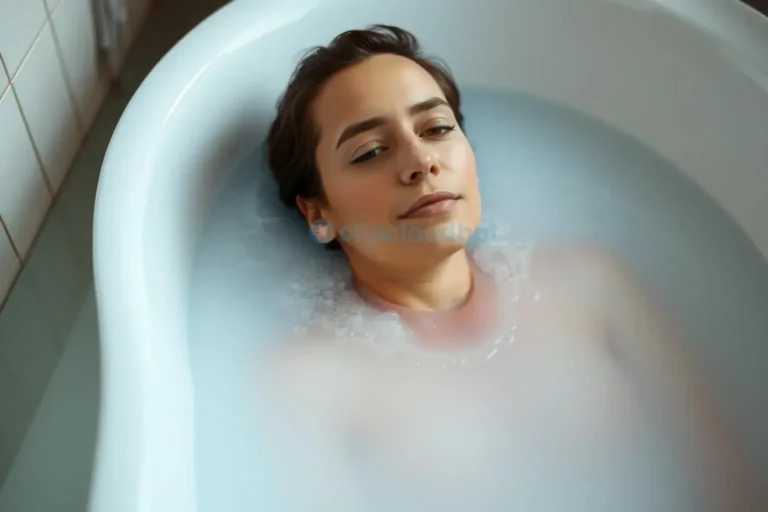
The Benefits of Heat: Relaxation, Detoxification, and Improved Mood
While cold exposure invigorates and boosts metabolism, heat therapy offers a contrasting yet equally valuable set of benefits, promoting relaxation, detoxification, and improved mood․ Heat application, whether through saunas, hot baths, or even warm compresses, has been utilized for centuries across various cultures for its therapeutic properties․ Unlike cold, which activates brown fat and boosts metabolism, heat works through different mechanisms to enhance well-being․
One of the primary benefits of heat therapy is its ability to induce deep relaxation․ Heat promotes vasodilation, widening blood vessels and increasing blood flow throughout the body․ This increased circulation delivers oxygen and nutrients to muscles and tissues, easing tension and promoting a sense of calm․ The warmth also soothes the nervous system, reducing stress and anxiety levels․ This relaxation response can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with chronic pain, muscle soreness, or sleep disturbances․
Beyond relaxation, heat therapy can also support detoxification processes․ Sweating, induced by heat exposure, is a natural mechanism for eliminating toxins and waste products from the body․ As sweat is produced, it carries with it impurities such as heavy metals and metabolic byproducts, helping to cleanse the body from the inside out․ This detoxification process can contribute to clearer skin, improved energy levels, and overall better health․
Furthermore, heat therapy can positively impact mood and emotional well-being․ The warmth and relaxation induced by heat can trigger the release of endorphins, natural mood boosters that promote feelings of happiness and well-being․ This effect can be particularly helpful for individuals experiencing low mood, depression, or seasonal affective disorder․ The soothing warmth can provide a sense of comfort and alleviate feelings of stress and anxiety, promoting a more positive emotional state․
Different forms of heat therapy offer unique advantages․ Saunas, for instance, provide dry heat that penetrates deep into the tissues, promoting intense sweating and detoxification․ Hot baths, on the other hand, offer a more immersive experience, allowing for full-body relaxation and muscle soothing․ Warm compresses can be targeted to specific areas of the body, providing localized relief from pain and inflammation․ Choosing the right method depends on individual preferences and therapeutic goals․
Incorporating heat therapy into a regular wellness routine can offer a range of benefits, from promoting relaxation and detoxification to improving mood and sleep quality․ Whether it’s a relaxing sauna session, a warm bath, or simply applying a warm compress, embracing the therapeutic power of heat can contribute to a healthier and happier you․ Combine heat therapy with other healthy lifestyle practices for a holistic approach to well-being․
Practical Applications: Integrating Cold and Heat Therapies into Daily Life
Integrating cold and heat therapies into your daily routine doesn’t require drastic changes, but rather mindful incorporation of small, manageable practices․ By strategically utilizing both cold and heat, you can harness their respective benefits and optimize both your physical and mental well-being․ These practices can range from simple adjustments to your shower routine to incorporating dedicated sauna or cold plunge sessions․
A readily accessible way to incorporate cold therapy is by ending your daily shower with a burst of cold water․ Start with a short duration, perhaps 30 seconds, and gradually increase the time as you acclimate․ This simple practice can invigorate the body, boost circulation, and even enhance mood․ For those seeking a more intense cold exposure, consider cold plunges in a tub filled with cold water․ Start with short immersions and gradually increase the duration as your tolerance improves․
Heat therapy can be easily integrated through regular warm baths․ Adding Epsom salts to your bath can further enhance relaxation and soothe sore muscles․ Sauna sessions offer a more intense heat experience, promoting profound sweating and detoxification․ If access to a sauna is limited, consider using a portable infrared sauna or even applying warm compresses to specific areas of the body for targeted relief․
Strategically combining cold and heat therapies can offer synergistic benefits․ For instance, alternating between hot and cold showers, known as contrast hydrotherapy, can further enhance circulation and reduce muscle soreness․ This practice involves alternating between short bursts of hot and cold water, stimulating blood vessel dilation and constriction, promoting blood flow and reducing inflammation․
Beyond these practices, consider incorporating other lifestyle habits that complement thermogenesis․ Regular exercise, particularly strength training, increases muscle mass, which contributes to thermogenesis․ Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods provides the necessary nutrients to support metabolic processes․ Prioritizing quality sleep allows the body to regulate its temperature effectively and optimize hormonal balance․
Listen to your body and adjust the intensity and duration of cold and heat therapies based on your individual response․ Start gradually and avoid extreme temperatures, especially if you have any underlying health conditions․ Consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any new therapeutic regimen, particularly if you have cardiovascular issues or other health concerns․
By thoughtfully integrating cold and heat therapies into your daily life, alongside other healthy lifestyle choices, you can harness the power of thermogenesis to optimize your metabolism, enhance your mood, and improve your overall well-being․ Embrace the contrast, experiment with different approaches, and discover the transformative potential of these ancient practices․