Nutrient Timing for Peak Performance
Strategically timing nutrient intake can optimize performance. Consume the right nutrients at the right time to fuel workouts and enhance recovery.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
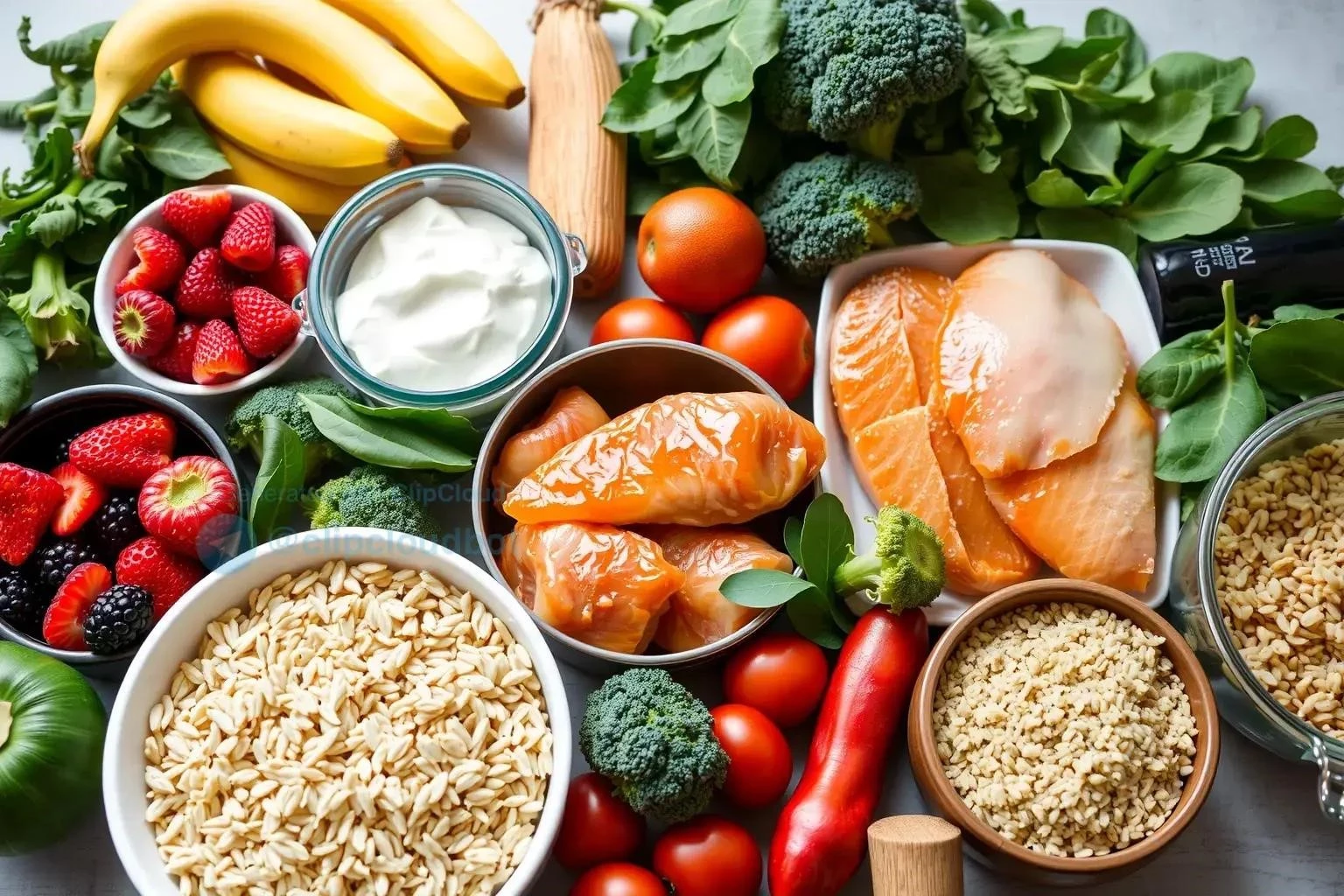
Fueling your body with the right nutrients before exercise is crucial for optimal performance. A pre-workout meal or snack should provide a readily available energy source, primarily from carbohydrates, while also including a moderate amount of protein and minimizing fats. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which your muscles use for fuel. Consuming carbs before a workout ensures you have adequate glycogen stores to power through your session. Protein helps to prevent muscle breakdown during exercise and supports muscle protein synthesis. Healthy fats, while important in the overall diet, should be limited pre-workout as they can slow digestion.
The timing of your pre-workout meal or snack is also key. A large meal should be consumed 2-3 hours before exercise, allowing ample time for digestion. For snacks, a smaller portion 30-60 minutes prior is ideal. Examples of effective pre-workout fuel include a banana with peanut butter, oatmeal with berries, or a small turkey and whole-wheat sandwich. Experiment to find what works best for your body and activity level.
Post-Workout Recovery
After intense exercise, your body needs to replenish glycogen stores and repair muscle tissue. Post-workout nutrition plays a vital role in this recovery process. The optimal window for nutrient intake is within 30-60 minutes after your workout, when your muscles are most receptive to absorbing nutrients. A combination of carbohydrates and protein is essential for maximizing recovery. Carbohydrates help to restore glycogen levels, while protein provides the building blocks for muscle repair and growth.
The ideal carbohydrate-to-protein ratio for post-workout recovery is generally around 3:1 or 4:1. Good post-workout options include a protein shake with fruit, Greek yogurt with granola, or a chicken breast with brown rice. Consuming adequate fluids is also crucial for rehydration after exercise. Electrolyte drinks or water can help replenish lost fluids and minerals. Prioritizing post-workout nutrition will help minimize muscle soreness, promote muscle growth, and prepare you for your next training session.
Macronutrient Timing Throughout the Day
Distributing your macronutrient intake strategically throughout the day can optimize energy levels, manage weight, and support overall health. While pre- and post-workout nutrition are crucial, considering your macronutrient needs at other times is equally important. Focus on consuming balanced meals and snacks that include a combination of complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats.
Prioritize protein intake at each meal to promote satiety and support muscle protein synthesis. Include complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables, for sustained energy release. Healthy fats, found in sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are essential for hormone production and cell function. Tailor your macronutrient ratios to your individual needs and activity levels. For example, individuals engaging in endurance training may require a higher carbohydrate intake, while those focused on strength training may benefit from higher protein consumption. By paying attention to macronutrient timing throughout the day, you can fine-tune your diet for optimal performance and well-being.
Eating for Sustained Energy
Sustained energy relies on balanced meals, regular eating habits, and proper hydration. Avoid energy crashes by making smart food choices.
Balancing Macronutrients for Stable Blood Sugar
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for sustained energy and overall health. Fluctuations in blood sugar can lead to energy crashes, cravings, and difficulty concentrating. Balancing your macronutrient intake plays a key role in regulating blood sugar. Focus on combining carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats in each meal and snack.
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide a slow and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes and crashes. Protein and healthy fats further contribute to blood sugar stability by slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates. Avoid consuming refined carbohydrates and sugary foods, as these can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar followed by crashes. By prioritizing balanced meals and snacks with a combination of macronutrients, you can maintain stable blood sugar levels and enjoy sustained energy throughout the day.
Hydration and Energy Levels
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal energy levels throughout the day. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, decreased cognitive function, and reduced physical performance. Water plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport, temperature regulation, and waste removal.
Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after exercise. Carry a water bottle with you and refill it regularly. Monitor your urine color as an indicator of hydration status – pale yellow urine indicates adequate hydration. In addition to water, electrolyte drinks can be beneficial during and after intense exercise to replenish lost minerals. Avoid sugary drinks, as these can contribute to dehydration and blood sugar fluctuations. Prioritizing hydration is a simple yet effective way to support sustained energy and overall well-being.
Hormonal Balance and Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in hormonal balance. Consuming nutrient-rich foods can support optimal hormone production and function.
Foods to Support Hormonal Health
Certain foods can positively influence hormone production and balance. Focus on incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into your diet to support optimal hormonal health. Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, contain compounds that can help regulate estrogen metabolism. Healthy fats, found in avocados, nuts, and seeds, are essential for hormone production.
Foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, support healthy digestion and can help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for hormonal balance. Lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, and beans, provide essential amino acids for hormone synthesis. Including these foods in your diet can contribute to overall hormonal balance and well-being. Consider consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations based on your individual needs and health status.
Meal Timing for Hormonal Regulation
The timing of your meals can also influence hormone levels. Consistent meal timing helps regulate your circadian rhythm, which plays a role in hormone production. Aim to eat meals and snacks at roughly the same times each day to establish a regular eating pattern. Avoid skipping meals, as this can disrupt hormone balance and lead to energy fluctuations.
Consuming a balanced breakfast within an hour of waking can help regulate cortisol levels, a hormone involved in stress response and metabolism. Distribute your meals and snacks evenly throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels and support hormone production. Avoid late-night eating, as this can interfere with sleep and hormone regulation. By establishing a consistent meal timing pattern, you can support healthy hormone function and overall well-being. Consider consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized guidance.